Carnosine is a dipeptide found in meat. It is not found in any plant foods. Dipeptide means it is made up of two amino acids, in this case beta-alanine and histidine.Carnosine concentrations are highest in muscles, brain, and central nervous system1 and gastrointestinal tract,2 This gives you an idea of its potential importance.
Unfortunately, it’s also one of the ten most common nutritional deficiencies, especially among vegetarians. If you are a vegetarian or vegan, you will have lower levels of carnosine in your muscles. This is one of the reasons why many strict vegetarians don’t compensate for this properly and often struggle to build muscle.
Carnosine also binds to advanced lipid oxidation end products (ALE) formed from oxidized seed oils in the diet, making it an important adjunct to linoleic acid (LA) detoxification.
Physiological effects of carnosine
Carnosine has a variety of physiological effects and benefits. For example, it:3
|
Provides exercise benefits—Approximately 99% of carnosine is found in muscle tissue, promoting lactic acid detoxification, improving muscle contraction and muscle relaxation, and increasing endurance |
|
Mitigating diabetic nephropathy by protecting podocytes and mesangial cells4 |
|
Modulate energy metabolism of macrophages and microglia by restoring and/or enhancing basal conditions |
|
Has antioxidant properties that scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and aldehydes produced by fatty acid cell membrane peroxidation during oxidative stress5 |
|
Regulate stem cell activity |
|
Regulate glucose metabolism |
|
Enhanced degradation and/or clearance of nitric oxide (NO) |
|
Promote wound healing |
|
Fight glycation6 |
|
Slow down the aging process by extending cell lifespan and maintaining cellular homeostasis7 |
|
Regulate osmotic pressure |
|
Regulates glutamate production and transport |
|
Regulate brain metabolism |
|
Chelated heavy metals8 |
|
As a pH buffer9 |
|
as a neurotransmitter |
|
Protecting olfactory receptor neurons in older adults |
Beef, liposomal carnosine and precursors are the best sources
Interestingly, a paper from June 202310 The science behind carnosine is reviewed in the medical journal Pharmaceuticals with the aim of developing new delivery systems for carnosine-based drugs. As stated in this article:
“This dipeptide has been studied in a number of experimental models due to its well-documented multimodal pharmacodynamic properties, including anti-aggregation, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, as well as the ability to modulate the energy metabolic state of immune cells. Diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, and clinical levels.
The main limitation of the therapeutic use of carnosine is related to its rapid hydrolysis… [This is the] This is why it is crucial to develop new strategies including chemical modification of carnosine or its carrier into innovative drug delivery systems (DDS) aimed at improving its bioavailability and/or promoting site-specific transport to different tissues. . “
Delivery systems currently in use or under development include intraperitoneal injections, intranasal sprays, and oral administration of various nanoformulations. But while the pharmaceutical industry is keen to figure out how to profit from making carnosine into drugs, you certainly don’t need a drug to get these benefits.
Simply eating organic, grass-fed beef is one of the most effective ways to increase your carnosine levels.11 This is one of the many reasons why cultured beef cannot replace real beef. Not only does fake beef lack carnosine, it also lacks B vitamins, retinol, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, taurine, creatine, and bioavailable forms of iron and zinc.12
Most carnosine supplements are also not very effective because carnosine is quickly broken down into its constituent amino acids by certain enzymes. Your body then reformulates these amino acids back into carnosine in your muscles.
One exception is liposomal carnosine, which seems to work very well. Another option is to supplement with beta-alanine, which is the rate-limiting amino acid in carnosine formation. According to a 2021 paper,13 Daily intake of beta-alanine can increase the carnosine content of skeletal muscles by as much as 80%.
Carnosine protects against LA-induced oxidative stress
One benefit not addressed in the pharmaceutical papers is the ability of carnosine to reduce LA-induced oxidative stress. Your body will slowly eliminate stored LA over time, but if you reduce your intake, carnosine can help reduce the oxidative damage caused by LA while your body cleans itself up. I take liposomal carnosine every day before meals to help with LA detoxification.
The omega-6 fat LA is highly susceptible to oxidation, and when the fat is oxidized, it breaks down into harmful subcomponents such as ALE and oxidized LA metabolites (OXLAM). These ALE and OXLAM are responsible for most of the damage.
Carnosine binds to ALE like a magnet and acts as a sacrificial pool. It’s basically a surrogate target for these profoundly damaging molecules. In this way, carnosine allows your body to eliminate ALE before it can damage your mitochondria, DNA or proteins. (Another molecule that may prevent damage caused by LA is carbon dioxide). The image below shows the role of carnosine in this regard.
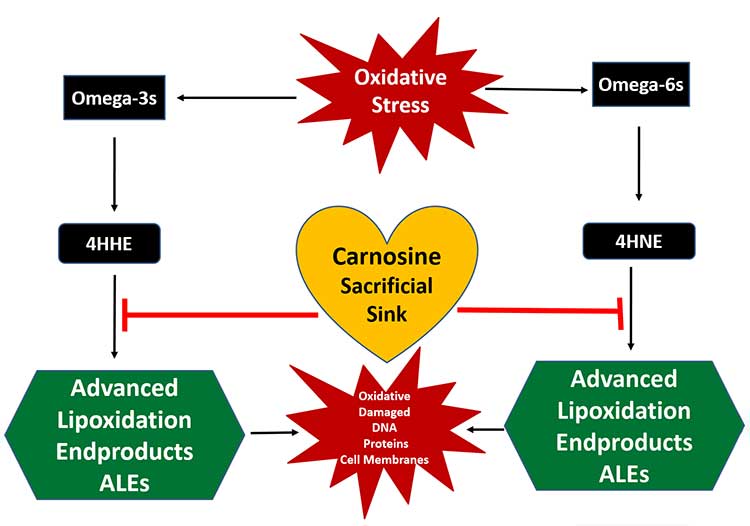
Carnosine can prevent many diseases
A 2021 paper published in the journal Antioxidants explains in more detail how carnosine protects against reactive oxygen species (ROS) and helps prevent oxidative stress-related pathologies:14
“A study on the effects of carnosine on oxidative stress in human renal tubular epithelial (HK-2) cells showed that carnosine reduced the expression of NADPH oxidase (NOX) 4 and increased the activity of total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD) , thereby reducing the expression of NADPH oxidase (NOX) 4, thereby reducing the production of intracellular ROS, alleviating cellular oxidative stress, and ultimately inhibiting the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis.
Carnosine has shown the ability to prevent pathologies characterized by oxidative stress in a variety of conditions… Carnosine alters the reactivity of superoxide anions by forming charge transfer complexes with superoxide radicals and reducing the efficiency of hydroxyl radicals , producing compounds that are less reactive than the hydroxyl radical.
One of the mechanisms that protect organisms against oxidative stress is the chelation of transition metals, preventing their participation in harmful processes involving ROS… Interestingly, when comparing metals involved in free radical generation, carnosine was found to have stronger antioxidant activity Copper is better than iron…
At physiological concentrations, carnosine reacts directly with superoxide anions, similar to ascorbic acid. Under physiological conditions, carnosine was found to reduce oxidative damage and increase the antioxidant activity of different antioxidant enzymes…
Experiments in aged rats showed that daily treatment with 250 mg/kg/carnosine significantly reduced oxidative stress and increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes… In a similar aged rat model, carnosine increased hepatic vitamin E, which is further evidence that Its importance in protecting liver health. Organisms are protected from free radical damage.
Growing data indicate that carnosine acts as a scavenger of reactive and cytotoxic carbonyl species, including 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE). HNE is an aldehyde produced endogenously by lipid peroxidation of unsaturated fatty acids, which acts as a “toxic second messenger” amplifying the harmful potential of free radicals.
HNE is considered an important biomarker of oxidative stress, and accumulating data suggest that it may modulate signaling pathways of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation. “
How Carnosine Prevents Alzheimer’s Disease
As pointed out in the Pharmaceuticals paper,15 One of the diseases carnosine can prevent is Alzheimer’s disease. In my November 2021 interview with Tucker Goodrich, he explained the role of HNE, specifically in Alzheimer’s disease, and why it’s so important to get rid of it.
“In heart failure, Alzheimer’s disease and AMD [age-related macular degeneration], one of the things they saw was that the cells couldn’t produce enough energy. Mitochondria are being damaged. HNE can cause this damage. It damages 24% of the proteins in cells, mainly those involved in energy production.
One of the ways cells produce energy is that they ferment glucose into pyruvate essentially outside the mitochondria. This is a completely normal part of metabolism, they produce a substance called pyruvate. A molecule called pyruvate dehydrogenase takes pyruvate into the mitochondria and converts it into acetyl-CoA so that the mitochondria can burn it very efficiently for fuel.
Well, one of the things that HNE does is disrupt the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase, which they find in Alzheimer’s disease because their cells are no longer able to produce enough energy. This is why your cells die in Alzheimer’s disease.
Beta amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease are induced by HNE. A great model proposed by Harvard University a few years ago demonstrates this.
Even the most critical and important part of the mitochondria, complex 5, ADP synthase (which takes all the energy from the mitochondria and converts it into ATP to power the rest of the body) is affected Damage of HNE. This is a big problem. When it comes to aging and health, there is no more fundamental problem than protein damage. “
Carnosine is the most potent scavenger of HNE, so optimizing your levels can go a long way toward preventing the damage caused by HNE that promotes Alzheimer’s disease.
Carnosine—a promising drug for the treatment of obesity-related diseases
Elevated HNE has also been found in obese and diabetic patients,16 Therefore, there is reason to suspect that carnosine may also be important in the treatment of these diseases. Another disease in which HNE is elevated is atherosclerosis. As stated in the 2021 Antioxidants Paper:number 17
“…Emerging research shows that these reactive aldehydes are more than simple markers of oxidative stress.
Conversely, these reactive species may play important causative roles in obesity-related diseases such as insulin resistance, and carnosine analogs may mitigate the production of reactive carbonyl species or enhance their removal, providing promising new therapeutic compounds for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Related to obesity. “
Take control of your health by reducing LA intake
As detailed in several previous articles, the evidence strongly suggests that excess LA is causing most, if not all, modern diseases, including heart disease and cancer. Fortunately, the solution is simple. Just lower your LA intake.
The easiest way is to use an online nutrition calculator (such as Cronometer) to calculate your daily intake. The Cronometer will tell you how much omega-6 you’re getting from your food, down to a tenth of a gram, and you can assume that 90% of it is LA. Anything over 10 grams may cause problems. My daily intake is controlled below 5 grams.
Since there is no harm in limiting LA, you want to keep it as low as possible by avoiding high LA foods. Remember, you can never reach zero, and you don’t want to. You do need some LA, but since LA is found in most foods and you only need small amounts, it’s virtually impossible to cause a deficiency.
